SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR
Working Principle of Synchronous Motor
A synchronous motor is based on the principle of magnetic interlocking.
The starting of a synchronous motor is the same as an induction motor initially excited by 3 phase AC supply given to the stator.
If the machine has gone to its maximum speed that is 90% of its speed, a DC Source is given to the rotor.
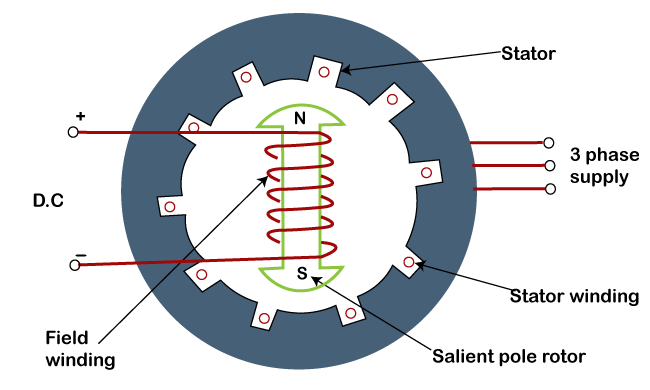
A 3-phase source is attached to the armature winding, and the armature develops a rotating magnetic field that rotates with a synchronous speed of 120f/P.
Once we excite the permanent poles of the field winding created by the DC source that tries to attract the unlike pole of the rotating magnetic poles.
If the magnetic poles are attracted and interlocked the rotor continues to rotate with synchronous speed.
Comments
Post a Comment