Electromagnetic or magnetic induction
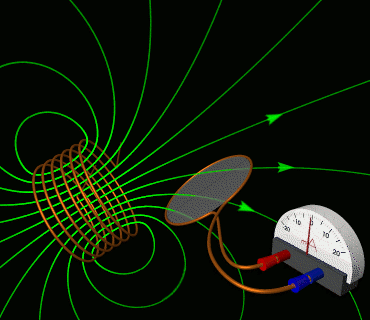
Alternating electric current flows through the solenoid on the left, producing a changing magnetic field. This field causes, by electromagnetic induction, an electric current to flow in the wire loop on the right.
Electromagnetic or magnetic induction is the production of an electromotive force (emf) across an electrical conductor in a changing magnetic field.
Michael Faraday is generally credited with the discovery of induction in 1831, and James Clerk Maxwell mathematically described it as Faraday's law of induction. Lenz's law describes the direction of the induced field. Faraday's law was later generalized to become the Maxwell–Faraday equation, one of the four Maxwell equations in his theory of electromagnetism.
Electromagnetic induction has found many applications, including electrical components such as inductors and transformers, and devices such as electric motors and generators.
It's good information sir
ReplyDeleteGood information sir. But the metre used in this is "galvanometer" know sir
ReplyDeleteYes , It is Galvanometer
DeleteSir; what is tha electromagnetic induction mcq?
ReplyDeleteIt is principle of of Electro Magnetic Induction which is basic principle of Motor, Generator and Transformer
DeleteWhen ever a conductor cuts magnetic field an EMF will induce.
Faraday invented these Laws Hence it is named as Faraday 's Law